Some parents are concerned that their kid’s adult teeth are yellow. Most of the time the reason for stained teeth is simple and does not require any treatment.
Why do teeth appear yellow?
The first reason is because they look more yellow next to their baby teeth. Baby teeth are so white that they are sometimes called ‘milk teeth’. When a new adult tooth is next to a baby tooth (milk tooth) they can look quite yellow. In this case it is normal and the colour difference will not be as noticeable when there are more adult teeth and less baby teeth.
Plaque and Dental Calculus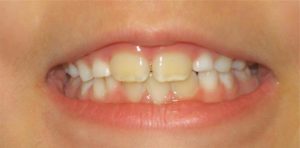
Another reason why kids teeth may appear more yellow is because they have plaque or ‘tooth germs’ on them. Plaque is a sticky yellowish film that forms on teeth. This needs to be removed daily through brushing and flossing to keep kids teeth healthy and prevent cavities. Calculus or tartar on teeth can also cause them to appear yellow. Tartar looks like a hard yellow substance stuck on your child’s teeth. It is more common for this to be on the lower front teeth. This cannot be removed by brushing alone, and the stained teeth need to be professional cleaned by a dentist.
Food and Drink Staining
Food and drink that are highly pigmented, such as blueberries, cherries, soft drinks or soy sauce, will result in stained teeth. The degree of tooth staining in children depends on whether they are regularly eating highly pigmented foods, and whether their tooth enamel was still being formed when during the period they were eating these foods. To prevent teeth yellowing and protect tooth enamel, it’s recommended your child rinse with water after consuming heavily pigmented foods or acidic drinks.
Teeth Trauma
Stained teeth can occur following an accident that damages the nerve in or near a tooth. The stain only forms within the tooth or teeth that the nerve is attached to. If your child has one tooth that is gray or yellow as a result of trauma to the nerve, they need immediate dental attention.
Fluorosis
Fluorosis is an irreversible condition caused by ingesting too much fluoride during the years when teeth are forming. The fluoride damages the enamel-forming cells, resulting in a mineralization disorder that increases the sub-surface enamel. The stained teeth turn a dingy yellow colour that can’t be removed.
Tetracycline (antibiotics)
Tetracycline is an antibiotic medication that can cause yellow teeth in children. These antibiotics are often found in cold medication. If the child takes these antibiotics during the child’s teeth forming years, the enamel can become permanently stained.
The enamel staining may affect the entire tooth, or it may affect parts of the tooth resulting in patches, lines or ribbons across the tooth. The extent and appearance of staining depends on the exposure and what part of the tooth’s enamel was being formed during that time the child took Tetracycline.
Tetracycline stains are impossible to remove without using bleaching techniques. To prevent this discolouration, children less than eight years of age are rarely prescribed Tetracycline.
Iron (Supplements/ Multivitamins)
Some children are susceptible to developing dark stains on their teeth from liquid iron supplements. These stains are temporary, however can be very difficult to remove.
To minimise teeth staining when your child has been prescribed a liquid iron supplement, you dilute the dose with water or juice and get your child to drink it through a straw. Ensure they rinse their mouth with water after taking their supplement, and regularly brush and floss to prevent colour build-up on the stained teeth.
To find out how to manage yellow teeth, read our follow up blog on management strategies and treatment for stained teeth.

Leave a Reply